1.1: Soluciones a problemas seleccionados del Capítulo 1
- Page ID
- 72400
P1.1:
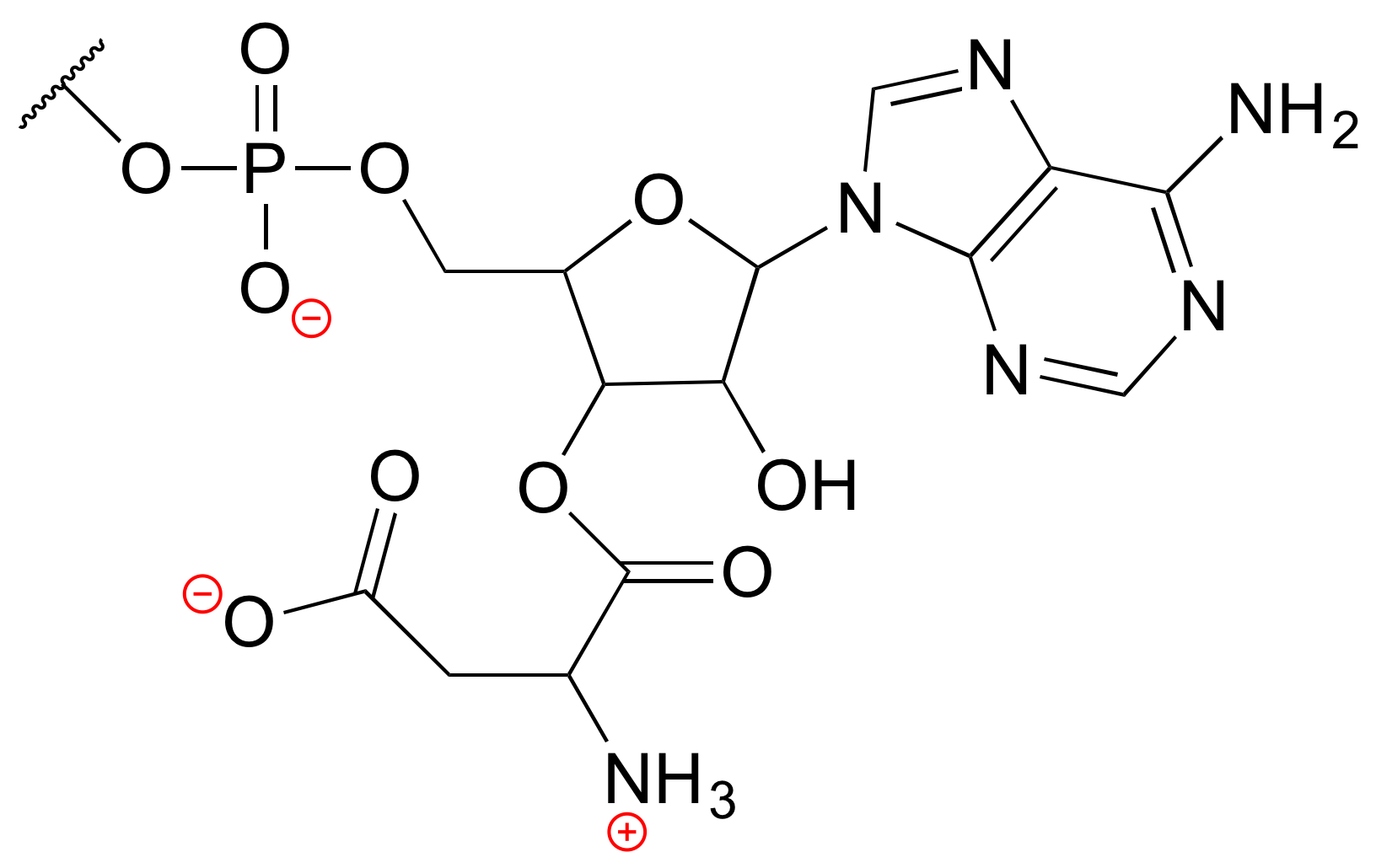
a) Los cargos formales se localizan como se muestra.
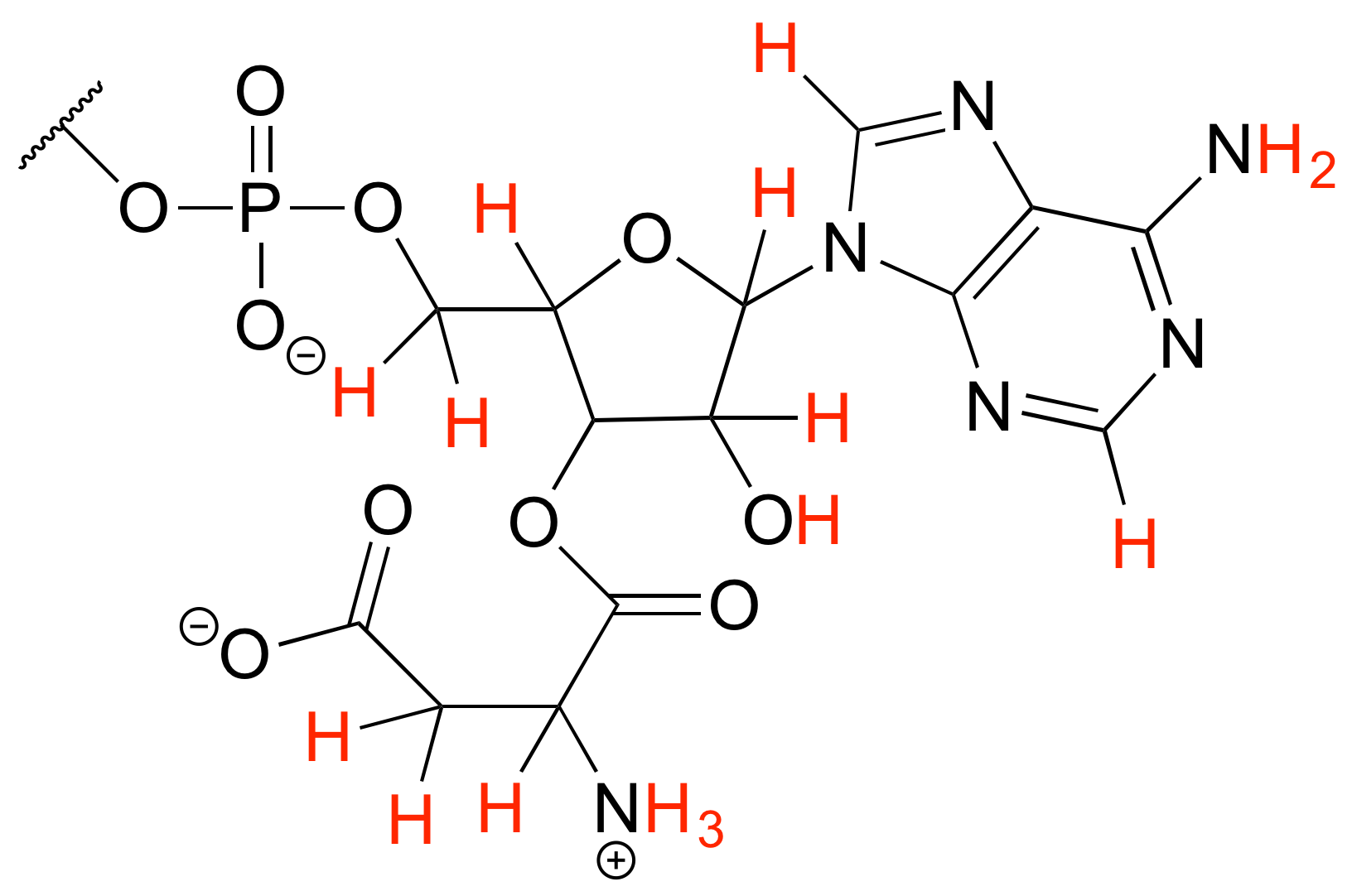
b) Hay 16 átomos de hidrógeno:
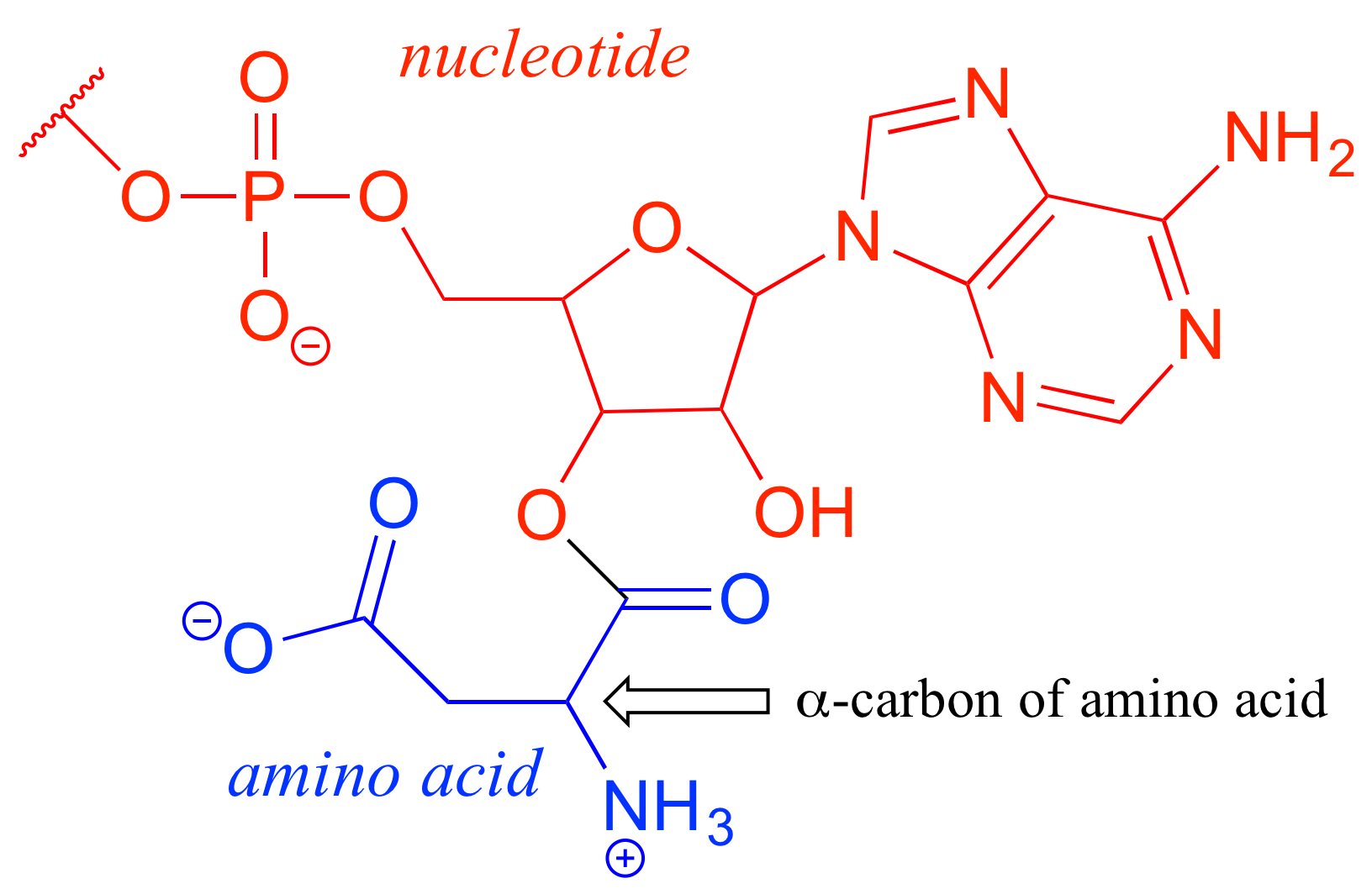
c) La estructura contiene un segmento de nucleótidos y un segmento de aminoácidos:
P1.4:
a)
Reacción A: aldehído a alcohol primario
Reacción B: Alcohol secundario a cetona; aldehído a alcohol primario
b) La segunda estructura de la derecha es una abreviatura apropiada. La parte de la molécula en la caja no cambia en la reacción, y esto se puede abreviar con 'R'.
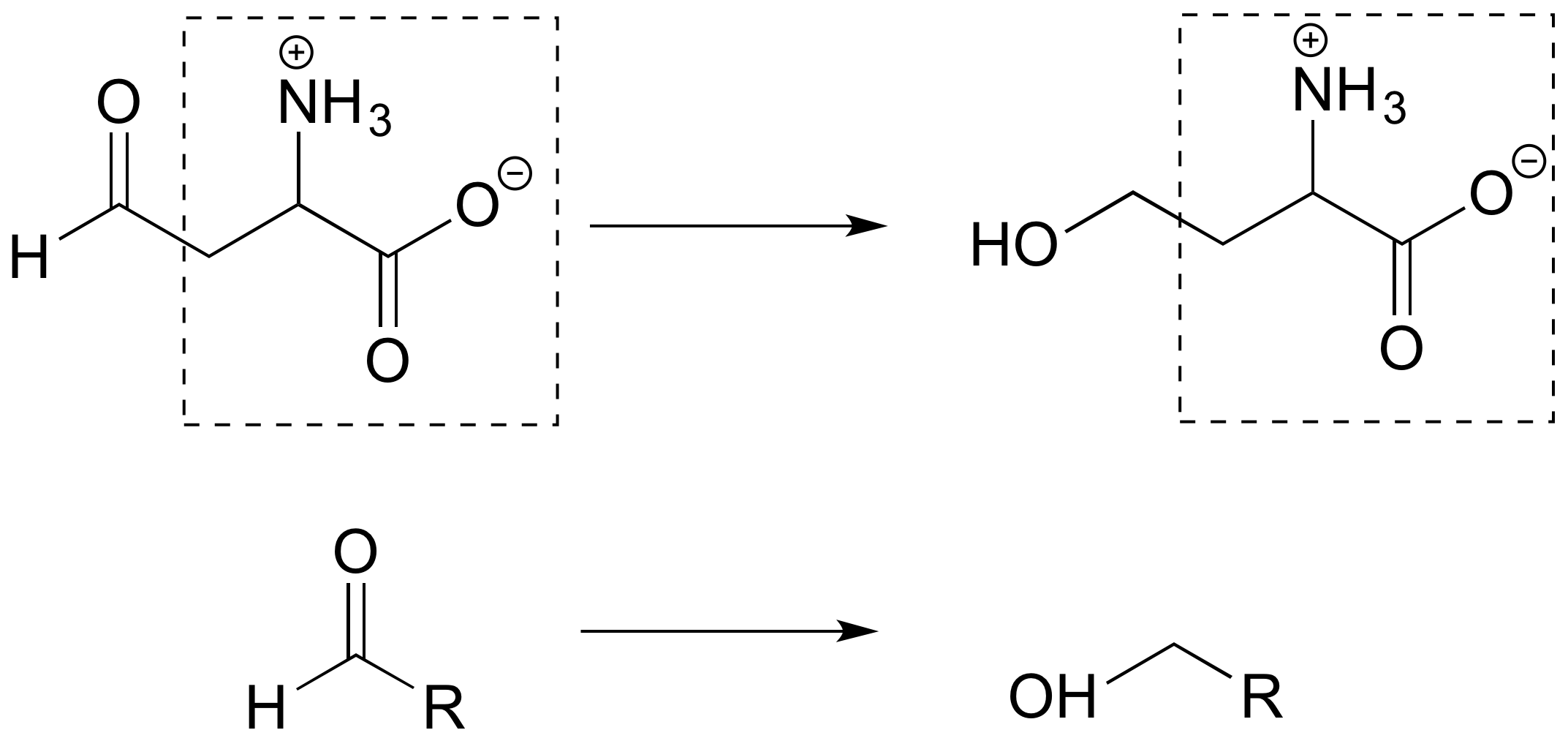
c) La parte de la molécula en la caja no cambia en la reacción, y ésta puede abreviarse con 'R'.
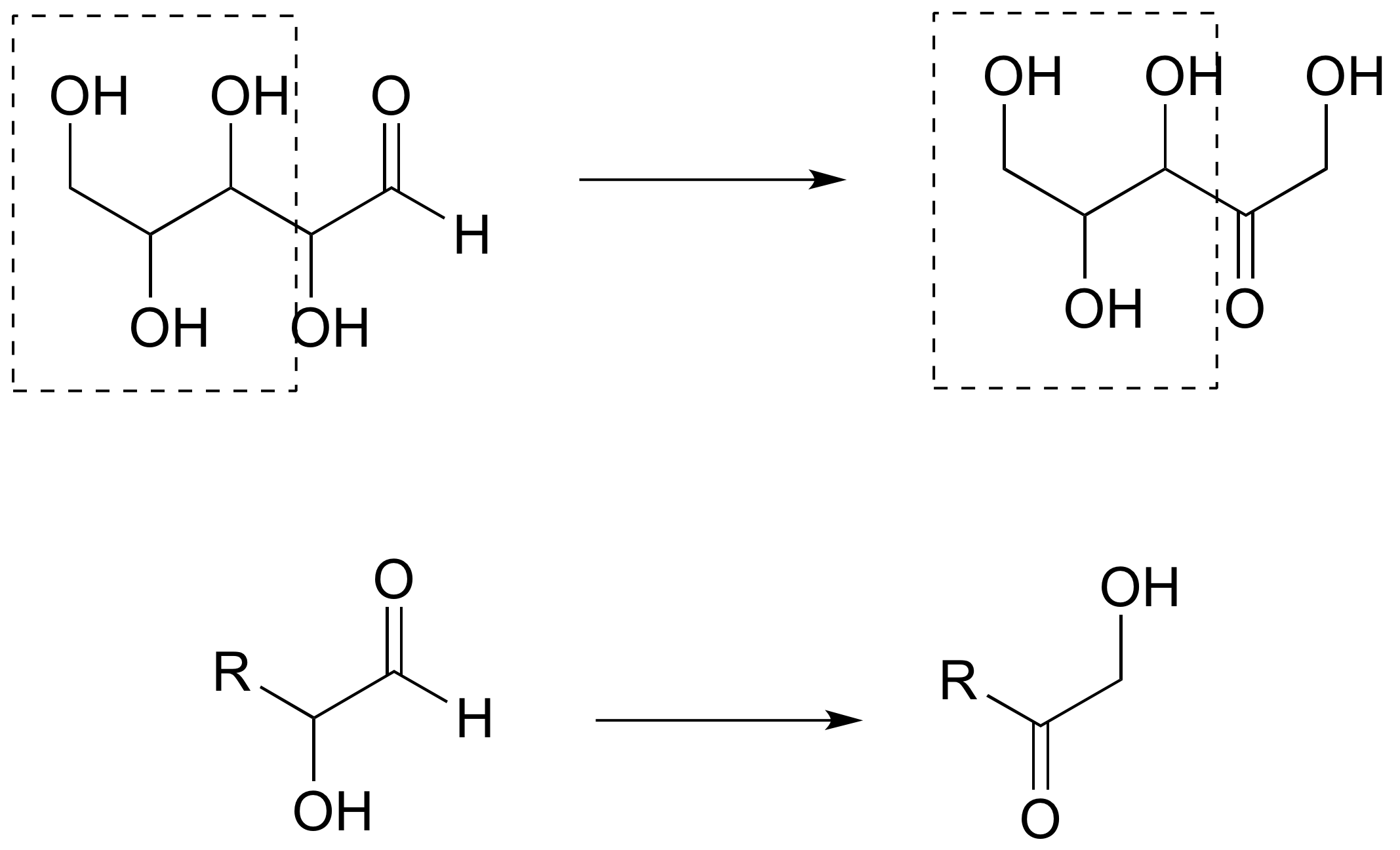
P1.5:
a) La treonina contiene un alcohol secundario.
b) La glutamina y la asparagina contienen amidas.
c) La cisteína contiene un tiol.
d) La metionina contiene un sulfuro.
e) La tirosina contiene un fenol.
f) La cadena lateral de lisina contiene un amonio primario.
g) Las cadenas laterales de glutamato y aspartato contienen carboxilatos.
h) La prolina contiene una amina secundaria.
P1.6: Tenga en cuenta que de acuerdo con la teoría VSEPR, el ozono tiene geometría doblada, el ion azida es lineal y la geometría alrededor de los átomos de oxígeno y carbono del bicarbonato está doblada.
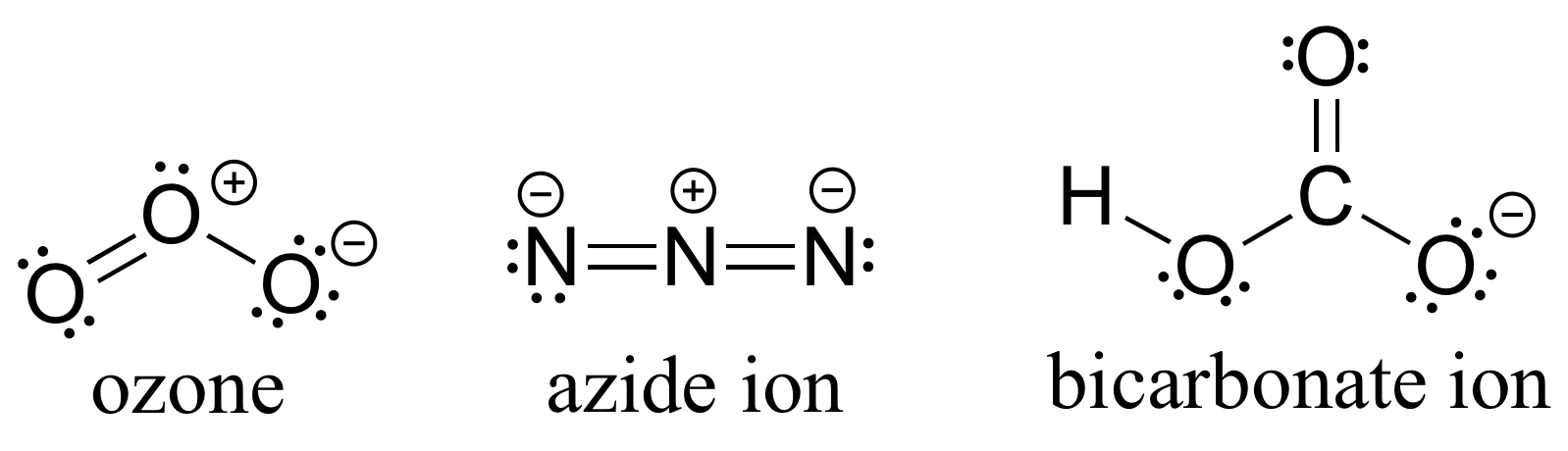
P1.8:
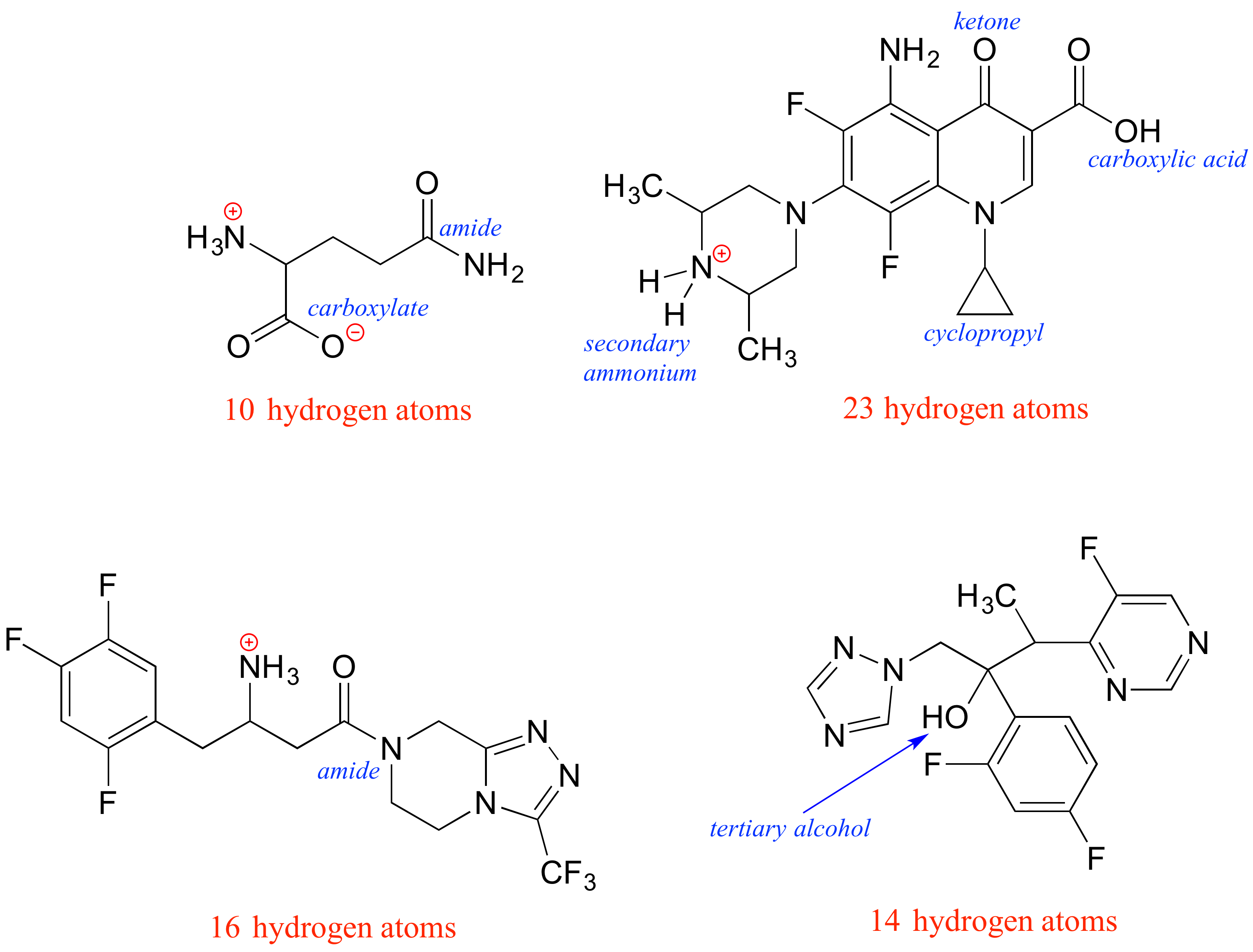
P1.10: